How the Directory Organizes Enterprise User Security Information:DNs and DITs |
 Contents |
 Previous |
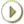 Next |
In a directory, each collection of information about an object is called an entry. For Enterprise User Security, elements such as users, roles, and databases are directory objects. Information about these objects are stored as entries in the directory.
Each entry in the directory is uniquely identified by a distinguished name (DN). The DN tells you exactly where the entry resides in the directory entry hierarchy, which is commonly called the directory information tree (DIT). The following image depicts the portion of the DIT where Enterprise User Security objects are stored in Oracle Internet Directory:
Referring to Figure: Enterprise User Security Directory Information Tree, an example of the DN for the "Manager" entry in the bottom of the figure is as follows:
cn=Manager,cn=OracleDefaultDomain,cn=OracleDBSecurity,cn=Products,cn=OracleContext
DNs are read from left to right, with the leftmost element of the DN representing the entry for the lowest node in the DIT.